The appearance of concave surfaces can vary depending on the shape and depth.
We observed relatively large concave shapes using various methods for comparison.
The samples are as follows:
1. USB memory connector section
2. Small engine part, φ5mm, with a screw in the 15mm deep section
3. Mechanical pencil lead holder section, φ5mm, with a depth of 6mm
 |
 |
 |
|
Observation using a standard high-definition microscope TG200HD2 (25 ~ 150x) |
 |
| 1. USB memory 2mm x 10mm, depth 8mm | |
 |
 |
| (30x) | (120x) |
| Even with a standard microscope, increasing the illumination to its maximum allows for relatively clear observation. | |
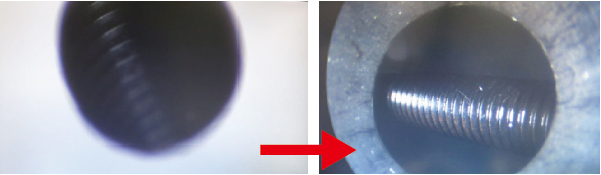
| 2. Small engine part, φ5mm, with a screw in the 15mm deep section | |
 |
Since the depth is 15mm, the light from a standard ring light has difficulty reaching the bottom, making observation challenging. |
| (80x) | |
| 3. Mechanical pencil lead holder section, φ5mm, with a depth of 6mm | |
 |
 |
| (30x) | (120x) |
| Increasing the magnification causes the image to become slightly darker. | |
| Changing the front ring light of the TG200HD2 to a smaller diameter (LED-16) version
By using a smaller diameter, the illumination angle becomes shallower, allowing the light to reach more easily. |
 |
| 1. USB memory | |
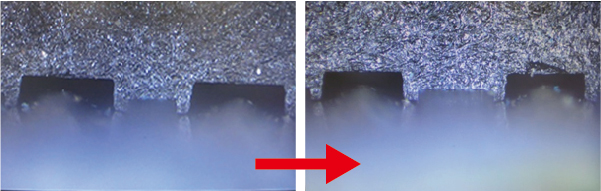 |
|
| 2. Small engine part | |
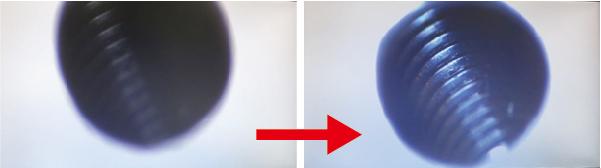 |
|
| 3. Mechanical pencil lead holder section | |
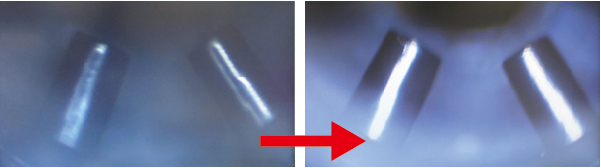 |
|
| Changing the lens to a borescope (rod lens) | |
| The borescope (rod lens) is available in sizes of φ4.0mm and φ2.7mm. |   |
 |
|