Supports megapixels that can take advantage of camera performance!
Compact size and ideal for embedded applications!
Coaxial lighting compatible, working distance 110 mm type
●Supports megapixels
●Single telecentric lens with structure centered on the face of the observer
●Compact size and ideal for embedded applications
●High-contrast design that allows you to clearly observe shadows and dark light, black and white
●Achieves low price while maintaining high performance
Specifications
※1 Calculated value calculated with a permissible circle of confusion diameter of 40 μm
※2 Theoretical resolution calculated at a wavelength of 550 nm
Main features
A telecentric lens is a lens that has a constant magnification at any position within the object distance.
There is no change in magnification within the depth of field.
There is no image distortion due to the field of view, and the accuracy of shape measurement of deep parts is greatly improved.
Features of telecentric lenses
1.Can be used as a medium to high magnification macro lens.
→ The price will be higher than the macro lens, but the performance will also be improved.
2.There is no expansion or contraction of the object within the depth of focus.
→Measurement error can be reduced when measuring dimensions.
3.You can reduce the ambient distortion due to parallax.
4.You can choose the focal length.
 |
(Short-distance type WD65mm and long-distance type WD110mm are available)
|
5.When used with coaxial lighting, uneven illuminance of the object can be reduced.
Non-coaxial type and coaxial lighting type are available
Example of use
Comparison between using a telecentric lens and using a macro lens
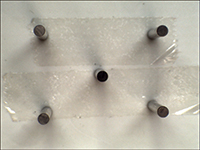
using a macro lens |
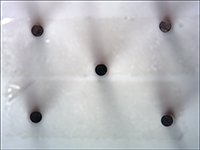
using a telecentric lens |
If you use a macro lens, the parallax between the center and the edge of the screen will be distorted even if you shoot the observation object from directly above.
However, when a telecentric lens is used, the distortion due to the parallax between the center and the edge of the screen is extremely small, accurate image information can be obtained no matter where the observation object is projected on the screen.