1. Prior preparation for observing and measuring metal structures
To observe metal structures under a microscope or a macroscope, prior preparation is necessary.
Generally, the following four types of preparatory methods are commonly used.”
①Sample sectioning
②Resin embedding (embedding)
③Polishing
④Etching process
2. Methods for each preparation step
① Sample sectioning
Large sample specimens are cut into smaller pieces using a cutting machine.
2. Methods for each preparation step
② Resin embedding
The cut sample specimens are solidified with resin.
The reasons and purposes for embedding in resin are as follows:
– Preservation of the edge shape of the sample specimen
– Maintenance of the shape to prevent deformation of the sample specimen
– Formation of a flat shape for easier observation
Various types of resin are available for curing, selected based on the material and characteristics of the sample specimen.
<Representative types of resin>
|
– Acrylic resin
|
 |
Each resin has different properties and colors, and their curing methods vary as well. There are various types such as thermoplastic, thermosetting, natural curing, UV light curing, and two-component mixing curing.
The sample is placed in a cylindrical case and solidified with resin. For heat curing, a heating embedding device is used, while for UV curing, UV light is irradiated.
Some observations may omit this step depending on the subject.
③ Polishing and mirror finishing
The surface of the metal sample specimen is polished.
Generally, a polishing machine is used.
There are manual and automatic types of polishing machines, with the former being suitable for experts and the latter for beginners.
Manual types tend to create uneven polishing due to variations in the pressure applied by hand to hold the sample, making them suitable for experts.
Automatic types, on the other hand, fix the sample specimen on a fixture and automatically polish it, resulting in more consistent polishing and making them suitable for beginners.
Using waterproof sandpaper, the sample specimen is polished from coarse to fine using a wet method (sprinkling water).
In precision polishing, cloth or buff polishing is used along with diamond slurry or alumina powder to achieve a mirror finish. Therefore, it’s necessary to change the grit of the waterproof sandpaper several times.
Polishing machines come in single-layer and two-layer types, with the latter being more expensive but more convenient.
④ Etching process (surface corrosion)
The polished surface of the sample specimen is immersed in etchant (corrosive liquid) suitable for its material and properties. Etching is performed for a specific time based on the concentration of the etchant and the material and properties of the sample specimen.
For example, in the case of graphitization, a 3% nitric acid alcohol solution (Nital solution) is used.
After etching, rinse the sample with water to remove the etchant, then clean with ethyl alcohol or similar solvent, and finally dry using a dryer or similar method.
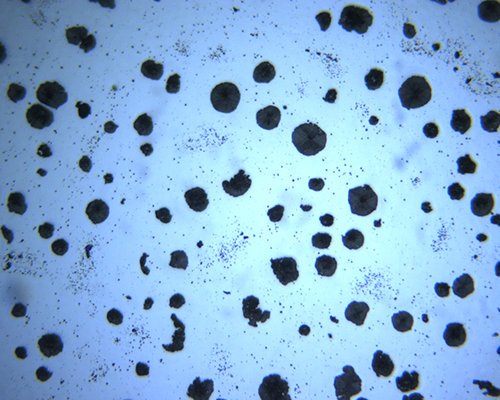 |
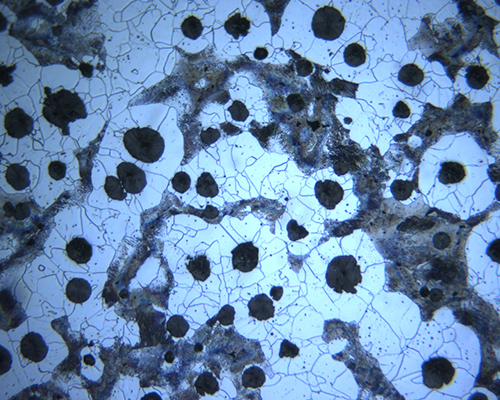 |
|
| Graphitization rate before etching |
|
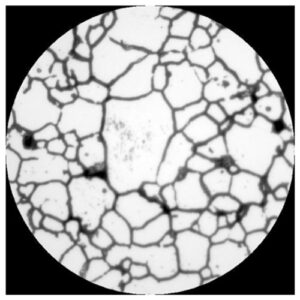
3. Microscopic Observation of Metal Structures
After undergoing the aforementioned preparation processes, metal structures can finally be observed. The polished surface of properly pre-treated sample specimens is observed under a microscope. By enlarging the structure and adjusting the focus, metal structures are examined.
At our company, we offer “metal microscopes,” “USB cameras for microscopes,” and packages combining metal microscopes with cameras.
For product details, please refer to the following.