The specifications of C mount camera always include “image size” and “image sensor size”.
In addition, this size is the value needed to calculate the field of view (when selecting the lens).
(To calculation of field of view, please refer to “f value of lens”.)
The use of “image sensor size”
You can also calculate the size of one pixel.
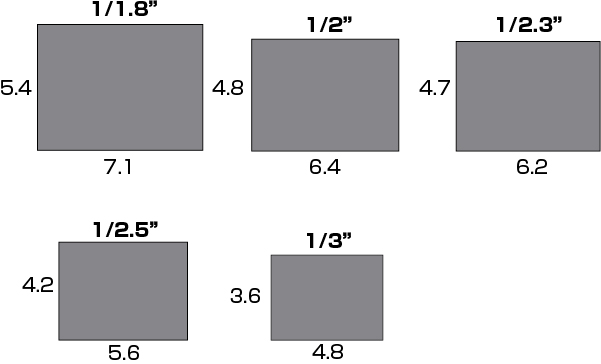
For example: The image sensor of 1 / 2.5 inch of 1.3 million pixels (1280 X 1024) is:
Horizontal 5.6 mm / 1280 pixels = 0.0044 mm / dot
Vertical 4.2 mm / 1024 pixels = 0.0041 mm / dot.
Image Sensor Size Meaning
Typically, when referring to monitor sizes, it indicates the diagonal length. However, the size of an image sensor is not measured diagonally.
For instance, in the case of a previously mentioned 1/2.5-inch sensor with 1.3 megapixels, the horizontal dimension is 5.6mm and the vertical is 4.2mm, resulting in a diagonal length of approximately 7mm.
However, the actual 1/2.5-inch sensor measures 10.16mm diagonally. This discrepancy originates from the historical representation of imaging tubes using vacuum tubes, where the size indication was based on the diameter of these tubes. Consequently, the size representation of image sensors has been aligned with this convention.
The Actual image sensor size
The practical use of imaging sensor size
The actual utilization of imaging sensor size pertains to the selection of the requisite lens and the calculation of the distance to the subject.
(1) In the case of CCTV lenses (fixed focal length lenses)
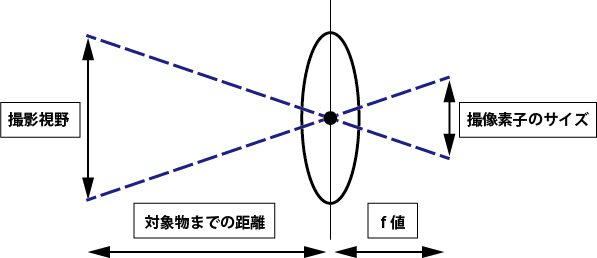
We shall calculate the required lens based on the desired dimensions of the subject to be captured. At this juncture, the essential factors are the “imaging sensor size of the camera” and the “distance to the subject (W.D.).”
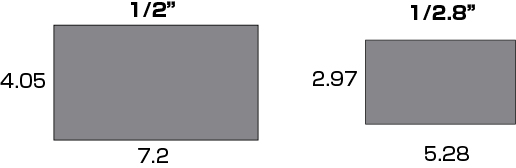
If we aim to ensure a vertical field of view of 300mm at a distance (W.D.) of 1 meter, what focal length lens should be selected? Assuming the use of a 1/2-inch camera sensor, the dimensions are as follows:
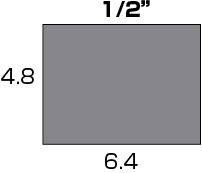
Imaging sensor size for a 1/2-inch camera:
The formula for the f-value is as follows:
f-value = (Distance to the subject (mm) × Vertical size of the imaging sensor (mm)) / Vertical field of view
By substituting the values:
f-value = (1000mm × 4.8mm) / 300mm = 16mm
By selecting a lens with a focal length of 16mm, the desired vertical field of view can be achieved.
The calculation for the horizontal field of view can be done in a similar manner.
By the way, if either the vertical or horizontal field of view is known, the other can be easily calculated without additional computations.
For a square-shaped imaging sensor with a 4:3 aspect ratio, as in this case, the horizontal field of view would be 300mm × 4/3 = 400mm.
(2) In the case of macro lenses
In the case of macro lenses used for capturing magnified images of subjects, the focal length is typically predetermined. In such instances, the f-value alone does not adequately represent the lens characteristics. Instead, the optical magnification is used as a measure.
For macro lenses, the optical magnification expresses the desired level of enlargement. With a lens at 1x (1:1 magnification), the observed field of view matches the size of the imaging sensor.
For example:
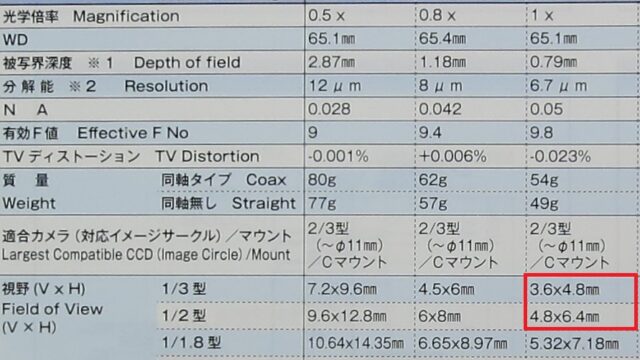
– For a 1/3-inch sensor, the dimensions are 4.8mm × 3.6mm.
– For a 1/2-inch sensor, the dimensions are 6.4mm × 4.8mm.
Considering these specifications, I recommend referring to our company’s macro lens specification sheet for more detailed information.
Additionally, when using a macro lens, the imaging sensor size is also utilized in calculating the overall magnification (the final magnification displayed on the monitor). The imaging sensor size plays a crucial role in determining the effective magnification of the captured image.
For more detailed information, I recommend referring to the concept of magnification in microscopes, as mentioned in the “Concept of Magnification in Microscopes” resource.
| USB Camera CS series | USB Camera DN series | GigE Camera | |
| 1/1.1 inch |
CS1200-GC(12MP・color) / CS1200-GB(12MP・monochrome) |
EG1200-GC(12MP・monochrome)/ EG1200-GB(12MP・monochrome) |
|
| 1/1.7 inch |
CS1200-C(12MP・color) / CS1200-B(12MP・monochrome) |
EG1200-C(12MP・color) / EG1200-B(12MP・monochrome) |
|
| 1/1.8 inch |
DN3RG-130(1.3MP・color) /
DN3RG-200(2MP color ) / 2MP – monochrome |
EG320-C(3.2MP color) / EG320-B(3.2MP monochrome)
EG600U-C(6MP color)/ EG600U-B(6MP monochrome) |
|
| 1/2.3 inch | DN3R-1000(10MP color) | ||
| 1/2.5 inch | CS500-C(5MP color) / CS500-B(5MP monochrome ) |
DN3R-500(5MP color) | |
| 1/2.9 inch |
CS41-C(0,04MP・color) / CS41-B(0,04MP・monochrome) |
EG41-C(0,04MP・color) / EG41-B(0,04MP・monochrome) |
|
| 1/2 inch |
CS130U-C(1,3MP・color) / CS130U-B(1,3MP・monochrome)
CS500U-GC(5MP・color) / CS500U-GB(5MP・monochrome) |
EG130U-C(1,3MP・color) / EG130-B(1,3MP・monochrome) |
|
| 1 inch |
CS2000-C(20MP・color) / CS2000-B(20MP・monochrome) |
EG2000-C(20MP・color) / EG2000-B(20MP・monochrome) |
|
| 2/3 inch |
EG501-C(5MP・color) / EG500-B(5MP・monochrome) |
Summary:
The imaging sensor size is a crucial value required for calculations such as “field of view” and “lens selection.” In the case of CCTV lenses, the f-value can be computed as follows to determine a lens that can achieve the desired vertical field of view:
f-value = (distance to the subject (mm) × vertical size of the imaging sensor (mm)) / vertical field of view.
For macro lenses, the imaging sensor size is utilized in calculating the overall magnification (the final magnification displayed on the monitor).